MANILA, Philippines – Since switching to a “healthier lifestyle” this month, Markie, a 33-year-old public school teacher, has noticed a flood of advertisements assuring him of a “safe and quick” way to lose weight.
An ad he found on social media “offered a drug with the same active ingredient as Ozempic,” the brand name of the drug used to treat diabetes and obesity in some countries. It has gained popularity among people who want to lose weight, leading to a global supply shortage as of 2022, including the Philippines.
READ: My life on Ozempic, the so-called ‘miracle drug’ for weight loss
According to the ad, those who take advantage of the offer for a one-time payment of P7,800 will be injected with the drug once a week for six weeks, subject to the approval of a doctor who can be consulted online. Once approved, the drug will be delivered to the patient’s home through a “free and discreet” service.
“It’s tempting, but I didn’t go through with it because I want my weight loss journey to be natural,” Markie told the Inquirer on Sunday.
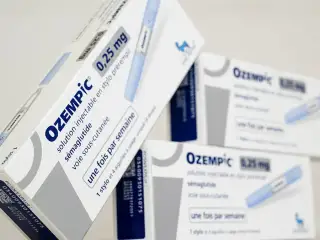
In its June 19 alert, the World Health Organization (WHO) warned of fake stocks of Ozempic (generic name: semaglutide).
READ: Risking lives for vanity
Multinational company Novo Nordisk confirmed that three batches of the popular drug “misrepresented their identity and source as they were not manufactured” by the company.
“serious risks”
The serial number LP6F832 is not recognized, the company said, while the combination of serial no. NAR0074 with serial number 430834149057 does not correspond to the original production data. The third group with number MP5E511 is original, but the product is counterfeit.
“The use of counterfeit Ozempic may result in ineffective treatment of patients due to incorrect dosing, contamination with harmful substances or the use of unknown or substituted ingredients,” the WHO said. “It may pose other serious health risks due to its potentially life-threatening subcutaneous injection administration.”
In the Philippines, Ozempic has been registered with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) since 2020, although diabetes patients have also complained of stock shortages, forcing some to turn to the black market.
While a single dose of Ozempic sells in big chain pharmacies for P7,650, the price can go up in online stores and unregulated social media markets.
On the other hand, a 500 mg tablet of metformin, which is the main first-line drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, sells for less than P4.
FDA spokeswoman Pamela Sevilla said earlier that Novo Nordisk had notified authorities in 2022 of a worldwide shortage of the drug due to a “sudden increase in demand due to off-label prescriptions” for weight loss.
Off-label prescribing occurs when a drug is prescribed to treat conditions other than those approved by the FDA. It is a legitimate and regular occurrence, especially in the treatment of unusual diseases and conditions.
“But the FDA does not have jurisdiction to regulate the decision of doctors if they use their clinical judgment to prescribe Ozempic for health conditions other than diabetes,” Sevilla said.
Your subscription could not be saved. Please try again.
Your subscription has been successful.
The FDA instead called on its parent agency, the Department of Health, as well as the Philippine Medical Association, to regulate how doctors prescribe Ozempic for off-label use.
#warns #fake #Ozempic #packs
Image Source : globalnation.inquirer.net